How to Repair Your Brain After Drug Use Updated
How to Repair Your Brain After Drug Use
The study of the human brain has made great progress in recent years. In 2015, for example, new discoveries were made in the link betwixt the brain and the allowed system, new details were revealed about how the brain changes equally we age and new insights were gained into the evolution of depression and diet, loneliness and even Facebook activity.
A more detailed agreement of the complexities of brain science helps united states of america better empathize how drugs work in the encephalon, equally well as their long-term implications of drug abuse and habit on both the brain and the trunk. Knowing the furnishings of drugs on the brain tin can lead to more effective ways of reversing the impairment.
How Your Brain Works
Your brain is a complex organ that runs everything virtually you. Your thoughts, memories, and personality traits are all housed in your encephalon. Your brain manages all of your physical functions — from climbing a mount to the involuntary chirapsia of your heart. In improver, all of your ideas — both conscious and unconscious — originate in your brain.
The brain works via a serial of physical structures that convey messages through brain chemicals. In some instances, messages are sent from the body through the nervous arrangement to the brain and back again. When you are walking barefoot and step on a pebble, for instance, the pain sensation is transmitted to your brain, and your brain responds with a message to option up your foot rapidly.
While your encephalon is handling pain responses, it'south also keeping your heart beating, regulating your body temperature and managing respiration. Your encephalon is the ultimate multitasker with some very of import responsibilities, and it manages all of this with a chemical messaging system.
Your brain uses neurotransmitters to send signals from cell to jail cell. There are several different types of cells in your encephalon that have unique functions. Receptors read the messages from the neurotransmitters. There are specialized receptors for each of the different neurotransmitters which fit together similar a lock and key.
Information is managed by the type and number of available receptors in the brain and the amount of the corresponding neurotransmitter produced. For a message to connect, the brain has to produce the neurotransmitter in a sufficient quantity, and that brain chemical has to come across upwardly with the right receptors. If the receptors are at that place merely happen to be blocked, the message volition non get through.
At that place are about 100 different types of neurotransmitters divided into iii categories: Pocket-size molecule, neuropeptides, and others. Once released, a neurotransmitter is available for a short time. If it does non bind to a receptor, it's either gobbled upwardly past enzymes or taken back into the neuron. A breakup of communication within the brain can result when these message chemicals are produced but not received.
One of the reasons neurotransmitters might not be received is that all the appropriate receptors are blocked. If a receptor is already engaged, it cannot take on a neurotransmitter. Receptor cells tin can but connect with their intended neurotransmitters, and just in a one-to-one relationship.
Complex thoughts are handled with a combination of neurotransmitters. By adjusting the variables — amount of neurotransmitter produced, number of bachelor receptor cells and possible combinations of neurotransmitters — your brain is capable of processing complex thoughts, similar emotions and abstract concepts.
With such great responsibilities, your brain is an extremely complex network of cells and chemicals that we continue to fruitfully study. While a lot of brain science is understood, there are still several questions to be answered.
Your circuitous encephalon is extremely precious to life as we know it, and warrants protecting.
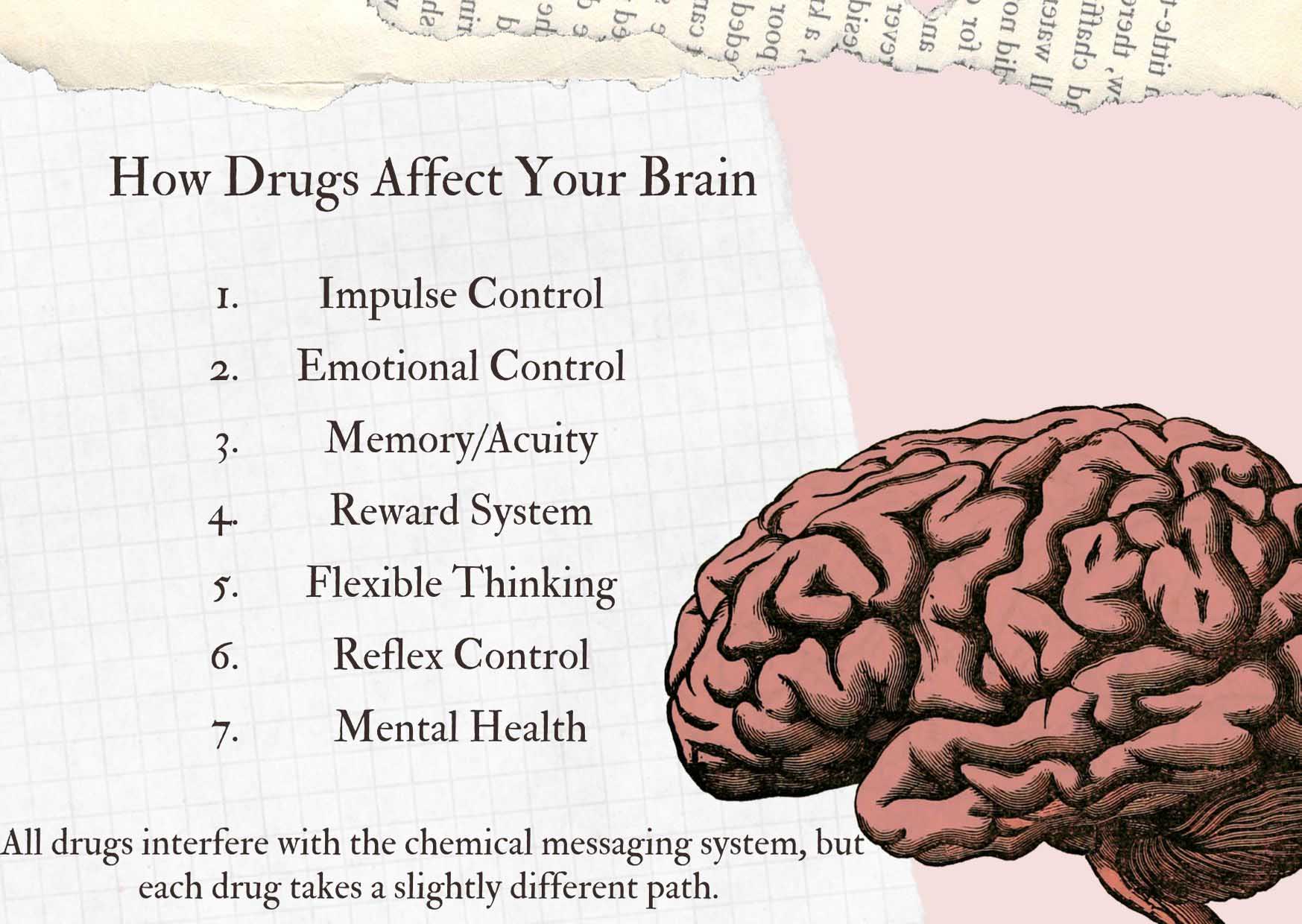
Parts of Your Brain
For ease of report and classification, the brain is divided into certain regions. Each region has a unique purpose, and yet, they all work together harmoniously.
 Cerebrum
Cerebrum
The largest role of the brain, the cerebrum is responsible for most of the work that the encephalon does. The cerebrum is divided into the left and right hemispheres, each containing the same subdivisions.
 Frontal Lobe
Frontal Lobe
The frontal lobe spans the front part of the head and is responsible for behavior, personality, creative thought, intellect, problem-solving, attention, olfactory property, muscle movements, abstract thinking, judgment, concrete reactions, and coordinated movements.
 Parietal Lobe
Parietal Lobe
The parietal lobe sits directly behind the frontal lobe and is subdivided into the sensory and motor cortexes. The sensory cortex receives information from the body about positioning, impact and pain. The motor cortex monitors and controls motion.
 Temporal Lobe
Temporal Lobe
The temporal lobe is located on either side of the head nigh the temples. The right and left temporal lobes are connected with axons. Language is the primary function of this lobe, in addition to speech and hearing. There is a specialized area within the temporal lobe that'south believed to be important in processing language, but more report is needed to explain specifically how it works.
 Occipital Lobe
Occipital Lobe
Vision is handled in the occipital lobe, located at the back of the head. Within the occipital lobe is a small surface area that specializes in facial expressions and understanding language.
 Cerebellum
Cerebellum
This is a pocket-sized region of the brain that handles some very bones functions. The cerebellum is responsible for rest, coordination, and movement. Its functions permit us to concur ourselves up and move in characteristically human means.
 Limbic System
Limbic System
A serial of glands, the limbic arrangement is located in the middle of the brain. Emotions and hormonal responses come from this part of the brain. The limbic organisation includes four primary glands: Thalamus, hypothalamus, amygdala, and hippocampus.
 Encephalon Stalk
Encephalon Stalk
The brain stem, the office of the brain that attaches to the spinal cord, manages basic life back up functions. The eye rate, respiration, and blood pressure are all controlled by the brain stem.
At that place is some overlap in functioning among the regions of the brain. Sure more circuitous concepts, similar language, are handled past coordination between different regions. This overlap in functioning tin exist good news when brain impairment occurs, due to accident or illness. Certain brain functions can be rebuilt when they are lost.
How Drugs Do What They Practice
No affair what type of drugs you utilise, whether they're pills prescribed by a medico or something you bought on the street to smoke, they eventually find their way to your brain. Smoking, swallowing, snorting, drinking, injecting or whatever combination of these will all deliver drugs to your bloodstream, which in turn moves them to your brain.
Since your brain manages all functioning and thoughts, it makes sense that a drug would have to travel to your brain to accept any upshot. Consider an over-the-counter coughing suppressant that relaxes the cough reflex, so you can become some sleep. That reflex is regulated past your brain, so the agile ingredient in the coughing medicine has to change the messages in your brain to be constructive.
Once in your brain, drugs interfere with your normal brain chemistry to produce the desired consequence. Considering the brain is and then circuitous, and our understanding of its functioning is not complete, drugs all accept side furnishings, every bit well. The cough suppressant reduces your cough and also makes yous drowsy. Every drug you take has more than i effect on you.
Commonly, drugs affect you mentally and physically. While alcohol reduces your inhibitions, information technology also depresses respiratory functions, for example. Side effects tin be the more unsafe part of any drugs since you're non looking for or monitoring them. Most people tend to focus on the master function of a drug and endeavor to ignore the side effects.
Your Brain and Behavior
Your brain controls your behavior in a number of ways. A reflex response, for instance, is the outcome of some quick situational assay in your central nervous system. Your brain makes yous motility your hand away from a hot stove to mitigate the damage of the burn to your pare.
Your brain also moves your muscles in response to diverse other cues, but most of these are uncomplicated thought patterns. Your brain adjusts your step when you walk upstairs, or up and downwards an incline. It finds you a place to sit when you are tired and moves yous to bed at the appropriate fourth dimension in the evening.
More circuitous behaviors are grouped together past psychologists as "executive behaviors," and they involve using emotional judgment to guide movements. These are the 8 executive behaviors governed by your encephalon and how their deficiency might affect functioning for an otherwise healthy developed:
 Task Initiation: Getting started with an activity
Task Initiation: Getting started with an activity
Without the ability to initiate, people become stuck in their electric current status. A deficiency in this area could keep someone from learning a new hobby or starting a new task. For smaller tasks, this can await like extreme procrastination.
 Cocky-monitoring: Evaluating your progress
Cocky-monitoring: Evaluating your progress
Evaluating your progress is essential to maintaining a clear connection with your own reality. A deficiency in this area would mean you were unable to take hold of your mistakes before someone else pointed them out to yous. This could be a large problem if that someone else is your boss.
 Organization: Keeping runway of items and ideas
Organization: Keeping runway of items and ideas
Some people are naturally more organized than others. A severe deficiency in organization could brand it difficult to carry on a coherent conversation and would result in lots of wasted fourth dimension looking for auto keys.
 Flexible Thinking: Adjusting to unexpected circumstances
Flexible Thinking: Adjusting to unexpected circumstances
The inability to accept new information would go far very difficult to learn annihilation. One time you develop a bad habit, it would also be difficult to change your thinking to change that habit.
 Impulse Control: Preceding actions with idea
Impulse Control: Preceding actions with idea
This is a huge problem in habit. When habit takes hold in your brain, you tend to follow your impulses rather than reason. A lack of impulse control tin can effect in risky behaviors and tin go very dangerous over time.
 Working Retentiveness: Holding onto of import data
Working Retentiveness: Holding onto of import data
Following a step-by-step procedure is a common power in near adults. When your working retentiveness is impaired, however, doing something as simple as remembering the directions to a friend's business firm can exist difficult. Without a working memory, there is an increased chance of dangerous behavior. Not remembering basic flammability properties, for example, might lead you to set a called-for cigarette downwards on top of the newspaper.
 Emotional Control: Managing feelings
Emotional Control: Managing feelings
If y'all struggle to control your emotions, you probably overreact in emotional situations. You might likewise human action out of those overblown emotions and create unnecessary drama and pain. Habit tin can cause a loss of emotional control considering nigh people nether the influence of drugs do not feel their emotions. When the drugs wear off, the emotional pain can be also much to process all at in one case. An addict volition often act out those emotions until he can calm them with more drugs.
 Prioritizing: Setting goals and making plans to come across them
Prioritizing: Setting goals and making plans to come across them
The inability to prioritize and programme tin can make life rather cluttered. Not realizing what is most important, you may take action on something impulsively, rather than applying your energy to necessary tasks. In the extreme, this could mean having a couple of drinks rather than being on time to pick your daughter up at school.
Although it is unclear exactly how the brain manages executive functions, it is possible to detect when the executive function system is not working. People with diagnosed mental disorders similar attention arrears disorder, autism and obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) showroom signs of impaired or under-developed executive functioning.
Recent studies have linked impaired executive performance with a higher risk of habit. Addiction tin can as well erode your executive functioning capacity, making it more difficult to recover from addiction.
 Your Brain's Pleasure Eye
Your Brain's Pleasure Eye
Literature on drugs and addiction often mentions the pleasure eye of the brain. In fact, pleasance is not perceived in but one area of the brain. There'south really a reward system in the brain that'southward made up of a group of interconnected glands and other structures, including many of the glands responsible for behavior. The pituitary gland is role of the reward system that circulates the feeling of pleasance throughout the trunk.
Your brain'south reward system is designed to reinforce positive experiences so you'll repeat those actions. It's like an internal conditioning machinery that incentivizes "good deeds" with pleasance.
How Dissimilar Drugs Work on Your Brain
While all drugs piece of work past getting into your brain and interfering with the chemic messaging system, each drug takes a slightly different path. There are a number of different means a drug tin can disrupt the natural messaging system in your brain and create the intended effect.
 Depressants
Depressants
Depressants are meant to accept a calming outcome and are used to reduce anxiety and induce relaxation. They wearisome downward brain action to eliminate racing thoughts, quick pulse, and rapid breathing. Some of the side furnishings of depressants are:
- Dizziness
- Confusion
- Slurred speech
- Poor concentration
- Fever
- Lack of coordination
- Depression
Depressants work with the brain chemical GABA that slows down encephalon function. By binding to the GABA receptors, depressants increase GABA action and thereby inhibit nerve transmissions. Depressants slow downwardly brain activity, which affects all of the systems in the body. With the brain working more slowly, vital functions as well slow down.
Some common depressants are:
- Seconal
- Amytal
- Ativan
- Valium
- Halcion
- Librium
- Klonopin
Street names for depressants include:
- Downers
- Barbs
- Reds
- Yellows
- Tooies
- Candy
- Sleeping pills
- Tranks
 Stimulants
Stimulants
The medical uses for stimulants have changed in recent years. Historically, they were prescribed for a diverseness of disorders, including respiratory issues such as asthma, several neurological disorders, and even obesity. Equally the dangers of stimulant abuse and habit became apparent, the medical uses for the substances were limited to narcolepsy, attention deficit disorder, and depression.
Popular prescription stimulants include:
- Ritalin
- Biphetamine
- Concerta
- Dexedrine
Street names for stimulants include:
- Uppers
- Black beauties
- Vitamin R
- R-ball
- Speed
- Kibbles and bits
- Truck drivers
- Skippy
The neurotransmitter associated with stimulants is dopamine, which is involved in pleasance, motion, and attending. When taken equally prescribed, stimulants increment dopamine levels in the brain slowly until they reach a level that produces the desired outcome. As recreational substances, stimulants raise dopamine levels quickly — much college and faster than could ever be achieved naturally.
The sudden increment in dopamine, a feel-proficient encephalon chemical, produces a euphoric outcome and increases the take a chance of addiction. By interfering with the advantage system, large doses of stimulants can create intense cravings. Concrete side effects tin include:
- Increased heart rate
- Increased body temperature
- High blood pressure
- Decreased ambition
- Difficulty sleeping
 Opioids
Opioids
Derived from opium, or synthesized to mimic certain substances found in opium, opioids were developed equally pain relievers. They cake pain by bounden to certain receptor cells in the encephalon and central nervous arrangement. With the opioids occupying the receptors, naturally occurring pain messages cannot get through.
Opioids send their own signals through those receptors that cause the brain to flood with dopamine, a feel-skilful chemic. The dopamine taps into the reward arrangement in the brain and accelerates addiction. Meanwhile, breathing is slowed every bit part of the pain-dulling message. The biggest danger posed by opioid overdose is a cessation of animate.
Common opioid pain relievers include:
- Morphine
- Vicodin
- Oxycontin
- Codeine
- Percocet
- Kadian
- Hydrocodone
Opioids are referred to by several different street names, including:
- Heroin
- Opium
- Horse
- Smack
- Guma
- Dream gun
- Zero
- Junk
- Black tar
- Midnight oil
 Cannabinoids
Cannabinoids
Cannabis is the agile ingredient in the hemp plant used for marijuana. The substance has likewise been replicated chemically in attempts to synthesize a drug with the same effects. Some people see synthetics equally a more controlled, measured mode of delivering the desired effects.
Cannabinoids produce a euphoric feeling and enhance sensory perception while creating irregular heartbeat, lack of focus and retention loss. Long believed to be rather harmless, cannabinoids have recently been more thoroughly studied. In the brain, marijuana and any other drug containing this chemical compound kills cells, shrinks neurons and causes Deoxyribonucleic acid fragmentation.
There are at least 85 different compounds that are considered cannabinoids and are naturally occurring in marijuana. Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD) are the two that producers concentrate on. THC has psychoactive properties, and CBD is believed to calm the nerves and also human action as an anti-inflammatory. Commercially grown marijuana plants are designed to produce college levels of these two compounds.
These drugs interact with the reward system in the encephalon. They increase dopamine activity, which is how they produce the euphoric feeling. Their actions in the reward organization are similar to that of morphine or nicotine — two drugs known to be extremely addictive. Indeed, habit seems to hinge primarily on the manipulation of dopamine in the reward organisation of the brain.
 Hallucinogens
Hallucinogens
This class of drug is aptly named considering it causes the user to hallucinate, hear sounds or see visions that are not existent. Hallucinogens interfere with the encephalon messaging systems involved in sensory perception and send erroneous signals. They work mostly in the forepart office of the cerebrum where mood, knowledge, and perceptions are processed.
Hallucinogens mimic serotonin, a neurotransmitter used to regulate appetite, digestion, sleep, sexual desire, memory, and mood, in order to demark with sure serotonin receptors. It is all the same unclear exactly how hallucinogens work, but research continues.
The effects of hallucinogens vary widely. Some users experience pleasant sensations and a deepened sense of understanding, while others have anxiety-ridden visions of terror. Hallucinogens besides produce some of these side furnishings:
- Sleeplessness
- Numbness
- Tremors
- Increased centre rate
- Nervousness
- Increased body temperature
- High claret pressure
- Relaxation
- Paranoia
LSD is probably the most widely known hallucinogen. Some others include:
- Psilocybin
- Peyote
- PCP
- Salvia divinorum
- MDMA
Here are some street names for hallucinogens:
- Acrid
- Barrels
- Large D
- Bluish heaven
- Boomers
- Purple flats
- Smears
- South parks
- Squirrel
- Vodka acrid
- Wedding bells
- Xanthous dimples
What Happens When You Take Multiple Drugs at Once?
Polydrug corruption — taking more than than 1 substance at a time — compounds the dangers. Drugs are hard to control, to begin with, but in one case they get into your encephalon, there are effects and side effects that y'all might not fifty-fifty be aware of. When you start combining drugs, the complications multiply.
Virtually drugs piece of work on levels in your brain. Consider booze and claret booze content (BAC). When you drink alcohol, your BAC increases for a catamenia of time. Eventually, the alcohol in your blood moves to your encephalon or is filtered out by your liver. Without a new supply of alcohol, your brain somewhen clears and goes dorsum to normal.
People who abuse alcohol tend to maintain a constant BAC, which becomes the new normal for their bodies. Because it is "normal," they don't realize that there's alcohol in their bloodstream — fifty-fifty before they have their starting time drinkable of the day. When they add some other drug on top of the alcohol, they're in danger of overdosing without fifty-fifty realizing information technology.
Many drugs deliver too much of a proficient affair when it comes to their interaction with the reward organization of the brain. Too much plus too much is scary unsafe. All of that pleasure sensation is just going to accelerate the addiction process that much faster. An overload of experience-skilful chemicals isn't going to feel very skillful when information technology wears off. The subsequent low afterward the high-high could be mortiferous.
Effects of Long-term Drug Use on Body and Encephalon
The human torso has a tremendous ability to adapt to changing conditions. All of your vital functions can exist measured within certain ranges. In other words, your body e'er seeks balance. When something becomes also high, adjustments are fabricated to return to center.
Consider, then, a drug whose side effects include increased heart charge per unit. When you put this drug in your system, your encephalon tries to lower your heart rate to make up the departure and maintain your heart inside the normal range. The more than y'all apply this drug, the more your encephalon has to recoup. Somewhen, y'all may accomplish a level of drug corruption where it becomes impossible for your brain to counteract these effects.
But in the meantime, your brain grows some new pathways to continually adjust your heart rate. It gets used to the presence of this drug and takes information technology as the new normal. The new pathways begin to hardwire your brain for maintaining your heart charge per unit within a normal range with this drug as part of the equation.
When you decide to detox and quit this drug use addiction, your brain goes into a spasm called withdrawal. It was used to operating with the drugs, and suddenly the drugs are withheld. You lot may crave medical intervention to maintain a reasonable heart rate while your brain readjusts to life without the drugs. It can be done, simply it takes time. The more changes that have occurred over time to the hardwiring of your encephalon, the longer it takes to abound new pathways to suit the new condition.
Heart rate is a adept example because it'south vital to life and because nearly drugs bear on it at some level. Many long-time drug users suffer damage to their heart or other vital organs. Living with an elevated middle rate for a long period of time has the effect of wearing out the muscle. When your heart doesn't role within normal ranges, oxygen and nutrients practise not broadcast throughout your body properly. Other vital organs cannot work optimally without their basic requirement.
It's similar to an engine running without gas and oil. The engine may still run without plenty oil, only information technology'southward sustaining damage that volition eventually kill information technology. The same might be true if you watered down the gas to brand information technology last longer. The engine might run, but information technology won't run well and information technology will be damaged by the time it quits.
Your encephalon continues to grow and alter throughout your adult life. By adding drugs, you force certain changes in your brain that are not natural and can be dangerous. When the drugs add feel-skilful chemicals to your brain, it stops producing them naturally in society to try to maintain a normal balance. Eventually, new pathways grow based on the lack of natural feel-good chemicals.
When negative thoughts become hardwired into your brain, a down spiral can begin. The brain follows habits just like y'all do. Through repetition, it tin can get in a groove, and then to speak, of negative thoughts. The more it uses those thought pathways, the deeper they become. Eventually, it tin be very difficult to abound new, more positive thought pathways.
Low is a major problem for long-term drug users. Since their good moods have been artificially induced for then long, their brains are non prepared to produce pleasure and happiness on their own. The brain can heal and regain its power for positive thinking, but the longer the drug utilise goes on, the harder it is to recover.

How Your Encephalon Teaches You to Keep Taking Drugs
Addiction is a complex concept that scientists continue to study and learn more about. Information technology'southward clear that the encephalon is the central control for addiction, and drugs create that addiction when they are inserted into the circuitous messaging system.
The nigh damage, in terms of habit, is done in the advantage system of the brain. The system is set up to encourage positive beliefs. It provides an incentive to repeat actions that are of import for survival. Procreation, for instance, is required for the continuation of our species, so sexual activity is rewarded with heightened pleasure responses. Eating is as well necessary for survival, and then there are good feelings fastened to that activity, too.
The whole thought of the reward system is to provide an incentive for repetition. When you lot do something good, the encephalon rewards y'all will a feeling of pleasure. The pleasance should entice y'all to repeat that activity. If you have a pick betwixt two actions, you are going to repeat the i that gave yous the most pleasance.
Drugs hijack this advantage organization and use information technology confronting you. When the drugs find their way into the reward system, they cause the brain to be flooded with dopamine or serotonin, ii feel-expert brain chemicals. The pleasure you lot get from this experience is remarkable considering many drugs exceed your natural ability to produce experience-good chemicals exponentially.
And then your drug-taking behavior is rewarded by your brain and it feels good. Even though the thinking function of your brain knows these drugs are harmful to your health and your life, information technology's difficult to override the extreme reward coming from your emotional brain. You begin to crave that farthermost pleasure again, but cypher else helps you achieve information technology.
Drug Use and Mental Illness: Confusion in the Brain
There is a reciprocal connection between drug abuse and mental disease. For some people, mental illness precedes addiction. Self-medicating to escape the symptoms of mental illness in not an uncommon path to addiction. Mental disease often comes with emotional pain and confusion that tin can exist mitigated temporarily with psychoactive drugs.
Self-medicating is never a good idea, however, for a number of reasons. Controlling or overcoming side effects without proper medical guidance is very hard. In well-nigh cases, when drug habit follows mental illness, the mental illness actually becomes worse.
Most mental illnesses have to do with aberrant brain chemical science. There is a lot going on in the brain, and just a minor divergence in one or two neurons or neurotransmitters tin can change brain functioning. Adding drug abuse to the mix, which too changes brain chemistry, will merely chemical compound the bug in the long run.
Mental illnesses demand to be professionally diagnosed and treated. In the presence of addiction, the mental illness cannot be properly assessed until the drugs are removed from the system. Encephalon chemistry is too complicated to diagnose in the presence of brain-altering substances.
Many substances of corruption actually make the addiction happen faster and more completely. By overstimulating the reward system in your brain, drugs create a stronger desire for increased pleasure than any natural occurrence. It is possible to become addicted to any happy experience, merely information technology will take a long time. in the instance of drugs that flood the encephalon with dopamine, the addiction comes very quickly because the brain is hardwired to want to echo pleasant experiences, and the high you get from something like cocaine is exponentially more than intense.
Reversing the Impairment After Long-term Utilise
Healing the damage caused by long-term drug abuse is a ii-step procedure. First, the changes in brain structures and chemistry that perpetuate the habit need to be reversed. Every bit long every bit the brain is working confronting recovery, we will be fighting a losing battle. The second step is to restore lost cognitive function.
There is evidence to suggest that, when the encephalon is flooded with dopamine from drug abuse, the dopamine receptors change in response. These structural changes that take identify in the encephalon make information technology more difficult for the receptors to read naturally produced dopamine, serotonin or any other neurotransmitter being mimicked by the drugs. The new receptors are specifically adapted to the compounds in the drugs and don't recognize their intended brain chemicals anymore.
These changes help increase the tolerance for the drugs that compels the user to increase size and frequency of doses. They also strengthen the cravings between doses. Essentially, this is the part of the brain where drug addiction is encouraged by the natural functioning of the brain.
The brain is capable of healing itself given the right conditions. Scientists are working to create therapies that facilitate encephalon healing. Certainly, ending the exposure to drugs is a showtime. Just like calculation the drugs caused the brain to modify and conform, by changing the conditions in the brain, nosotros can stimulate a re-adjustment.
The cardinal to this approach, of form, is to control cravings and then the brain can remain drug-gratis. It'due south as well important to provide medical support until the brain is capable of maintaining all vital functions once more. During the detox period, the encephalon goes through a type of shock where it doesn't know exactly what to do. It cannot go on on its current class, just it does not remember how information technology worked before the drugs.
Scientists have also discovered that the brain is capable of working around any damaged areas. This ability is referred to every bit "plasticity," and information technology allows the brain to continue to function even when thought pathways are damaged from jail cell death. The brain tin grow new pathways and movement its messages around a unlike route. The brain actually has tremendous flexibility this way.
Plasticity is like losing your right mitt in an accident and learning to write with your left. Since many encephalon functions are spread out over dissimilar areas of the brain, information technology's possible to build new language skills, for instance, when the original center of linguistic communication has been destroyed. Encephalon cells are also capable of regeneration, so in time the losses can be minimized.
Although the amount of damage to the brain from long-term drug abuse tin be extensive, the possibilities of healing always exist. The first step, of grade, is to eliminate the drugs. Getting help for addiction equally soon every bit possible will minimize the damage and speed the healing.
Get Help At present

Chris Clancy is the in-house Content Manager for JourneyPure'southward Digital Marketing team, where he gets to explore a wide diversity of substance corruption- and mental health-related topics. He has more than 20 years' feel equally a journalist and researcher, with strong working knowledge of hospital systems, health insurance, content strategy, and public relations. He lives in Nashville with his wife and 2 kids.
How to Repair Your Brain After Drug Use
Posted by: henriquezbale1966.blogspot.com

0 Response to "How to Repair Your Brain After Drug Use Updated"
Post a Comment